Title : Two new papers on 55 nm Bipolar-CMOS-DMOS SPADs
link : Two new papers on 55 nm Bipolar-CMOS-DMOS SPADs
Two new papers on 55 nm Bipolar-CMOS-DMOS SPADs
The AQUA research group at EPFL together with Global Foundries have published two new articles on 55 nm Bipolar-CMOS-DMOS (BCD) SPAD technology in the upcoming issues of IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Quantum Electronics.
Engineering Breakdown Probability Profile for PDP and DCR Optimization in a SPAD Fabricated in a Standard 55 nm BCD Process
Link [open access article]: https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/stamp/stamp.jsp?tp=&arnumber=9543572
Abstract:
CMOS single-photon avalanche diodes (SPADs) have broken into the mainstream by enabling the adoption of imaging, timing, and security technologies in a variety of applications within the consumer, medical and industrial domains. The continued scaling of technology nodes creates many benefits but also obstacles for SPAD-based systems. Maintaining and/or improving upon the high-sensitivity, low-noise, and timing performance of demonstrated SPADs in custom technologies or well-established CMOS image sensor processes remains a challenge. In this paper, we present SPADs based on DPW/BNW junctions in a standard Bipolar-CMOS-DMOS (BCD) technology with results comparable to the state-of-the-art in terms of sensitivity and noise in a deep sub-micron process. Technology CAD (TCAD) simulations demonstrate the improved PDP with the simple addition of a single existing implant, which allows for an engineered performance without modifications to the process. The result is an 8.8 μ\mu m diameter SPAD exhibiting ∼\sim 2.6 cps/ μ\mu m 2^2 DCR at 20 ∘^{\circ} C with 7 V excess bias. The improved structure obtains a PDP of 62% and ∼\sim 4.2% at 530 nm and 940 nm, respectively. Afterpulsing probability is ∼\sim 0.97% and the timing response is 52 ps FWHM when measured with integrated passive quench/active recharge circuitry at 3 V excess bias.
On Analog Silicon Photomultipliers in Standard 55-nm BCD Technology for LiDAR Applications
Link [subscription needed]: https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9739982
Abstract:
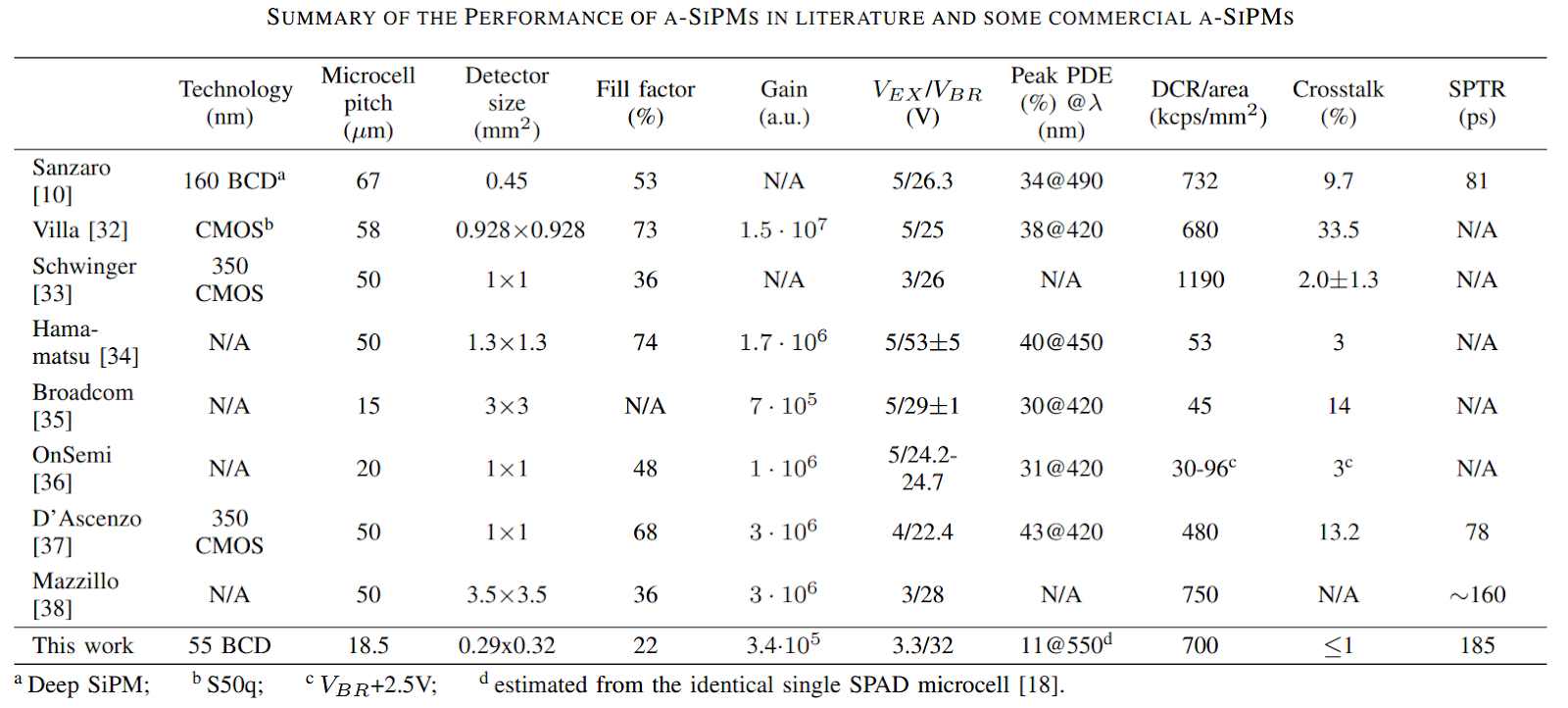
We present an analog silicon photomultiplier (SiPM) based on a standard 55 nm Bipolar-CMOS-DMOS (BCD) technology. The SiPM is composed of 16 x 16 single-photon avalanche diodes (SPADs) and measures 0.29 x 0.32 mm2. Each SPAD cell is passively quenched by a monolithically integrated 3.3 V thick oxide transistor. The measured gain is 3.4 x 105 at 5 V excess bias voltage. The single-photon timing resolution (SPTR) is 185 ps and the multiple-photon timing resolution (MPTR) is 120 ps at 3.3 V excess bias voltage. We integrate the SiPM into a co-axial light detection and ranging (LiDAR) system with a time-correlated single-photon counting (TCSPC) module in FPGA. The depth measurement up to 25 m achieves an accuracy of 2 cm and precision of 2 mm under the room ambient light condition. With co-axial scanning, the intensity and depth images of complex scenes with resolutions of 128 x 256 and 256 x 512 are demonstrated. The presented SiPM enables the development of cost-effective LiDAR system-on-chip (SoC) in the advanced technology.
Thus Article Two new papers on 55 nm Bipolar-CMOS-DMOS SPADs
That's an article Two new papers on 55 nm Bipolar-CMOS-DMOS SPADs This time, hopefully can give benefits to all of you. well, see you in posting other articles.
You are now reading the article Two new papers on 55 nm Bipolar-CMOS-DMOS SPADs with the link address https://caronrepiyu.blogspot.com/2022/04/two-new-papers-on-55-nm-bipolar-cmos.html




0 Response to "Two new papers on 55 nm Bipolar-CMOS-DMOS SPADs"
Post a Comment